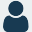
De-extinction technology has taken a significant leap forward as Colossal Biosciences announces the successful resurrection of the dire wolf, an extinct species that roamed North America over 12,000 years ago. By leveraging advanced techniques like cloning and gene editing, you can now explore the implications of this groundbreaking achievement in biotechnology, which not only highlights our growing understanding of genetics but also raises important questions about the ecological role of de-extincted species in todayҳ world.
Key Takeaways:
Colossal Biosciences successfully created three dire wolf pups using ancient DNA, cloning, and gene-editing technologies, marking the first instance of de-extinction for an animal species.
The dire wolves, imperatively hybrids of gray wolves and their extinct relatives, were produced by altering the genetic makeup of gray wolves to exhibit traits specific to Aenocyon dirus.
The project has sparked a debate in the scientific community regarding the ethical implications and ecological roles of resurrected species, especially in light of current challenges faced by living wolf populations.
Background on Dire Wolves
While many may associate dire wolves with the fantasy series Ӈame of Thrones,Ԡthese large canids were once real predators that roamed North America approximately 250,000 years ago until their extinction around 12,500 years ago. With a size larger than that of modern gray wolves, dire wolves were formidable hunters, showing a significant adaptive prowess across various habitats.
Characteristics of Dire Wolves
Any aspiring naturalist would find dire wolves fascinating due to their unique physical traits. They typically boasted a wider head, a robust jaw, and thick, light fur, enabling them to thrive in diverse climates as top predators.
Extinction and Historical Significance
By understanding the extinction of dire wolves, you can appreciate their historical role in North Americaҳ ecosystems. As major predators, they influenced the populations of various prey species and contributed to the ecological balance of their time.
Even today, the extinction of dire wolves raises questions about biodiversity and conservation. Their disappearance around 12,500 years ago coincided with the arrival of humans and climate shifts, highlighting the delicate balance of ecosystems. Their demise serves as a reminder of how species interact with one another and the environments they inhabit, emphasizing the need for thoughtful approaches to wildlife management in our current era.
#image_title
Colossal Biosciences
Any discussion about the resurgence of extinct species must includeThe Return of the Dire Wolf. Colossal Biosciences, a Dallas-based biotech company, proudly announces its achievement as the worldҳ first to successfully de-extinct an animal. By leveraging advanced techniques like cloning and gene editing, scientists have brought forth three dire wolf pups, marking a significant milestone in the field of de-extinction.
Company Overview
Along with its innovative approach, Colossal Biosciences was founded in September 2021 by entrepreneur Ben Lamm and Harvard geneticist George Church. The company has made headlines not only for its work on dire wolves but also for its ambitious plans to resurrect other extinct species, including the woolly mammoth and dodo. It has attracted over $435 million in funding to support these revolutionary projects.
Previous Projects in De-extinction
Across various initiatives, Colossal has explored the boundaries of de-extinction technology. The company is particularly invested in reviving species like the woolly mammoth, aiming to introduce the first calves by 2028. Additionally, it has successfully produced cloned red wolves, which highlights its commitment to advancing genetic technologies for conservation purposes.
In fact, the challenges presented by the mammoth project and cloning of red wolves underline Colossalҳ focus on not just resurrecting extinct animals but also aiding endangered species. Their approach involves extensive genetic analysis and editing, ensuring that the efforts are scientifically sound while considering ethical implications, such as animal welfare and ecosystem balance.
The De-extinction Process
For the first time, Colossal Biosciences has successfully resurrected an extinct animal through a meticulous de-extinction process that combines ancient DNA analysis, cutting-edge gene editing, and cloning techniques. By leveraging these innovative technologies, the team has brought the dire wolf back to life, showcasing the remarkable potential of biotechnology to reverse extinction processes.
Ancient DNA Utilization
Any DNA extracted from ancient fossils, such as those of the dire wolf, provides imperative insights into its genetic makeup. Colossal utilized genes from a 13,000-year-old tooth and a 72,000-year-old skull to construct high-quality genomes, allowing scientists to identify specific traitslinked to the dire wolfҳ appearance and behavior.
Gene Editing Techniques
Among the numerous advanced methods employed, CRISPR technology played a significant role in revising the gray wolf genome to replicate dire wolf traits. The team focused on altering 14 genes through 20 precise edits, creating a hybrid that mirrors the extinct speciesҠdefining characteristics.
Another important aspect of the gene editing process is the ethical considerations that guide it. Colossal has taken steps to mitigate any potential complications by carefully selecting genetic alterations that promote desirable traits while minimizing risks. This thoughtful approach ensures that the dire wolf puppies not only exhibit physical attributes of their prehistoric ancestors but also presents a responsible model for future de-extinction efforts.
Cloning and Birth of Dire Wolf Pups
Despite the challenges associated with de-extinction, Colossal Biosciences successfully birthed three dire wolf pups, marking a historical milestone in the field. Utilizing advanced cloning techniques, the company merged ancient genetic material with living cells to create a hybrid resembling the prehistoric dire wolf, Aenocyon dirus, to bring these extinct giants back to life.
Clone Production Method
Among the techniques employed by Colossal, CRISPR gene-editing played a significant role in altering gray wolf cells and integrating traits specific to dire wolves. The team carefully edited 14 genes and then cloned promising cell lines, which were implanted into surrogate dogs, ultimately leading to the birth of the pups.
Details of the PupsҠBirth
Pups were born on October 1, 2024, and January 30, 2025, showcasing the successful implementation of the cloning process. Their births were the outcome of a novel technique that enabled the development of these newly engineered canines.
Birth records indicate that two male pups arrived first, followed by a female three months later. Each pup was carefully monitored within a secure, 2,000-acre facility, ensuring their health and well-being. The success of these births not only demonstrates the effectiveness of Colossalҳ methods but also paves the way for future endeavors in de-extinction and conservation efforts.
#image_title
Ethical Considerations
Your interest in de-extinction raises important ethical questions. As scientists commence on efforts to bring back species like the dire wolf, the potential impacts on existing ecosystems and animal welfare must be carefully evaluated. While the allure of reviving lost species captivates many, ethical discussions emphasize responsibility in creating and managing these hybrids, particularly concerning their ecological roles and interactions with current wildlife.
Criticisms of De-extinction Efforts
One major criticism of de-extinction efforts is the substantial financial resources required, which some argue could be better allocated to conservation initiatives for endangered species. Critics worry that focusing on resurrecting extinct creatures diverts attention from pressing environmental issues and complicates the dynamics of existing ecosystems, ultimately compromising biodiversity.
Animal Welfare Measures
Against these criticisms, Colossal Biosciences emphasizes their commitment to animal welfare in their de-extinction projects. They have implemented numerous precautionary measures to ensure the well-being of both the resurrected dire wolves and the surrogate animals, striving to address ethical concerns while advancing their scientific goals.
Due to their focus on responsible practices, Colossal has established a facility certified by the American Humane Society, where the welfare of the animals is a top priority. This facility is equipped with advanced security and monitoring systems, ensuring a safe environment for both the newly created dire wolves and the surrogate dogs used in the cloning process. By eliminating risky genetic edits and conducting thorough screenings, they aim to mitigate potential health issues and ensure ethical transparency in their groundbreaking work.
Implications for Conservation
After the successful resurrection of the dire wolf, you might wonder about its implications for conservation efforts. Colossal BiosciencesҠachievement opens new discussions on de-extinction technologyҳ potential to restore lost species and impact biodiversity. As highlighted in a recent article about how the dire wolf returns from extinction, you can explore more about these developmentshere.
#image_title
Potential Impact on Endangered Species
By showcasing de-extinction technology, Colossalҳ work could lead to innovations that benefit endangered species, like the critically endangered red wolf. Using similar cloning techniques, you may see these approaches positively influence conservation strategies.
Role of De-extinct Species in Ecosystems
Beside the potential benefits for conservation, you should consider how de-extinct species might fit into current ecosystems. The reintroduction of organisms such as the dire wolf raises questions about their ecological roles and interactions.
In addition to fostering interest in de-extinction, you need to be aware that reintroducing species like the dire wolf could disrupt existing ecological balances. Understanding the specific role these resurrected animals might play is crucial. For example, will they compete with gray wolves or interact differently with their environment? These dynamics are vital for evaluating whether such initiatives genuinely aid conservation or complicate it further.
Final Words
Presently, you can observe how Colossal Biosciences has achieved a groundbreaking feat by successfully resurrecting the dire wolf, marking a significant milestone in de-extinction efforts. This innovation not only highlights advancements in genetic technology but also raises important questions about the ecological implications and ethical considerations of bringing back extinct species. As you follow this development, consider the potential roles these creatures might play in your environment and the broader implications for conservation efforts.
FAQ
Q: What method did Colossal Biosciences use to resurrect the dire wolf?
A: Colossal Biosciences utilized a combination of ancient DNA extraction, cloning, and gene-editing technology to resurrect the dire wolf. They extracted DNA from two dire wolf fossils, allowing them to assemble high-quality genomes. Bycomparing these genomes with those of living canids, they identified specific genetic traits associated with dire wolves and made 20 edits in 14 genes of gray wolf cells. These modified cells were then cloned and transferred into donor eggs, with the resulting embryos carried by domestic dog surrogates. This process resulted in the birth of three dire wolf pups.
Q: Why is the resurrection of the dire wolf significant professionally and scientifically?
A: The resurrection of the dire wolf is significant as it marks the first successful attempt to de-extinct a species, representing a major advancement in genetic engineering and conservation science. It showcases the capabilities of CRISPR technology and other scientific techniques to manipulate genomes, raising important discussions about species revival and the ethical considerations accompanying such efforts. Moreover, this achievement paves the way for future de-extinction projects, including potential contributions to the conservation of endangered species by utilizing similar technologies to improve genetic diversity and health.
Q: What are the potential ecological implications of bringing back the dire wolf?
A: The ecological implications of resurrecting the dire wolf are currently uncertain and debated among scientists and conservationists. While Colossal Biosciences aims to reintegrate these animals into ecosystems, critics express concern about the feasibility of such an endeavor. With existing challenges in maintaining healthy gray wolf populations, it is questioned whether dire wolves could occupy an ecological niche in modern environments. Additionally, considerations regarding animal welfare, interspecies competition, and habitat impacts must be assessed before any reintroduction efforts are undertaken.
Related Posts
Post Overlay 07
Trump Trial Live Updates: Jury Selection in Hush Money Case
The Real MVPs of the Iranian Attack: Israelҳ Air Defense Systems
Team 03
Home 04
Contact
The postDire wolf de-extinction: Colossal Biosciences says it has resurrected an extinct animal for the first time first appeared onThe Stone Builders Rejected.
The postDire wolf de-extinction: Colossal Biosciences says it has resurrected an extinct animal for the first time first appeared onThe Stone Builders Rejected.
Dire wolf de-extinction: Colossal Biosciences says it has resurrected an extinct animal for the first time