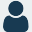
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) carriers are specialized ships designed to transport LNG, a super-cooled liquid form of natural gas, across vast oceans. These vessels are engineering marvels, equipped with sophisticated cryogenic technology to maintain the LNG at its extremely low temperature (-162°C or -260°F) during transit. Their ability to safely and efficiently transport LNG has revolutionized the global energy market, enabling the delivery of natural gas from remote production sites to consumers worldwide.
The design of LNG carriers is centered around the safe containment of the cryogenic cargo. These ships employ double-hull construction and advanced insulation systems to minimize heat transfer and prevent boil-off, the evaporation of LNG due to heat absorption. The cargo tanks, typically spherical or membrane-type, are constructed from specialized materials like aluminum or stainless steel, which can withstand the extreme temperatures and pressures of LNG.
The propulsion systems of LNG carriers are also highly specialized. Initially, steam turbines were the primary propulsion method, utilizing the boil-off gas as fuel. However, modern LNG carriers increasingly employ dual-fuel diesel-electric (DFDE) engines or slow-speed diesel engines with reliquefaction plants. These systems offer improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, contributing to more sustainable LNG transportation.
The loading and unloading of LNG are critical operations that require specialized infrastructure and equipment. LNG terminals are equipped with cryogenic pipelines, storage tanks, and loading arms to transfer the LNG between the ship and onshore facilities. The transfer process is carefully controlled to minimize boil-off and ensure safety.
The size and capacity of LNG carriers have increased significantly over the years, driven by the growing demand for LNG and the need for economies of scale. Modern LNG carriers can transport over 170,000 cubic meters of LNG, equivalent to the energy needed to power a small city for several months. The development of larger and more efficient carriers has reduced transportation costs, making LNG a more competitive energy source.
The LNG carrier industry is subject to stringent safety regulations and standards to minimize the risk of accidents and environmental damage. International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations and industry best practices govern the design, construction, and operation of LNG carriers. The use of advanced safety systems, such as emergency shutdown systems and gas detection systems, ensures the safe transportation of LNG.
The future of LNG carriers is closely tied to the growth of the global LNG market and the transition to cleaner energy sources. The development of more efficient and environmentally friendly propulsion systems, such as those powered by boil-off gas or hydrogen, is a key area of research. The integration of digital technologies and automation will further enhance the safety and efficiency of LNG transportation. The continuous innovation in LNG carrier technology will play a crucial role in meeting the world's growing energy demand while minimizing environmental impact.